5 Ways To Use AI Voices In Your eLearning Courses
Audio is transforming the way we consume information online. The explosive growth of audiobooks and podcasts in recent years clearly demonstrates the appetite and benefits of offering audio content. Advancements in Machine Learning on the other hand have led to significant improvements in voice technology, making modern AI voices sound unbelievably realistic. And with benefits such as instant text-to-audio conversion, multiple languages, and scalability, they offer a perfect solution for the eLearning industry.
Using AI voices one can convert text-based educational content into a more convenient audio format, making it possible for students to learn by listening while they are multitasking, on the go, or when they are just tired of staring at screens. But it's not just the busy, on-the-go students who benefit, people who are visually impaired, suffering from reading disabilities or dyslexia benefit the most because audio accessibility is essentially their primary channel of taking in information.
The accessibility benefits of AI voices go a long way in helping students learn more productively and efficiently through audio, but they can also offer a more engaging learning experience when implemented the right way. And as a course creator, when you integrate audio you are potentially increasing your reach and catering to a wider and diverse audience who otherwise might not have enrolled due to accessibility limitations. So how can one use AI voices to create audio content for their courses?
Accessing AI voices
First, we need access to AI voices. Only a handful of companies offer high-quality, realistic AI voices. Robotic or monotonous voices make the listening experience rather dull and uninteresting. Therefore, it is important that the voices sound realistic. The realism and human-like quality are what make the modern voices magical.
According to Datamation, Amazon and Google are the leading providers of AI voices in the market today followed by IBM and Microsoft.
There are two ways of accessing AI voices from these companies:
- Programmatic access
This involves creating developer accounts on Amazon or Google and using their APIs (Application Programming Interface) to programmatically send textual content and get back raw audio that you can either embed in your courses or share directly with your students as MP3 files. - Non-programmatic access
This uses tools that have already integrated with different voice providers and offer their AI voices under one easy-to-use UI that doesn’t require any technical knowledge to create audio.
Once you have access to the AI voices and are able to convert text to audio, here are 5 ways you can use the audio in your eLearning courses:
1. Make Audio Versions Available Alongside Written Content
The benefit of having the same content in audio and written form is that it allows students to simultaneously read and listen to the text, which has shown to contribute positively to students’ perceptions and level of engagement and can be quite advantageous in terms of learning outcomes.
Course content such as lessons, notes, and key information that is usually in the form of written text can be easily converted into audio.
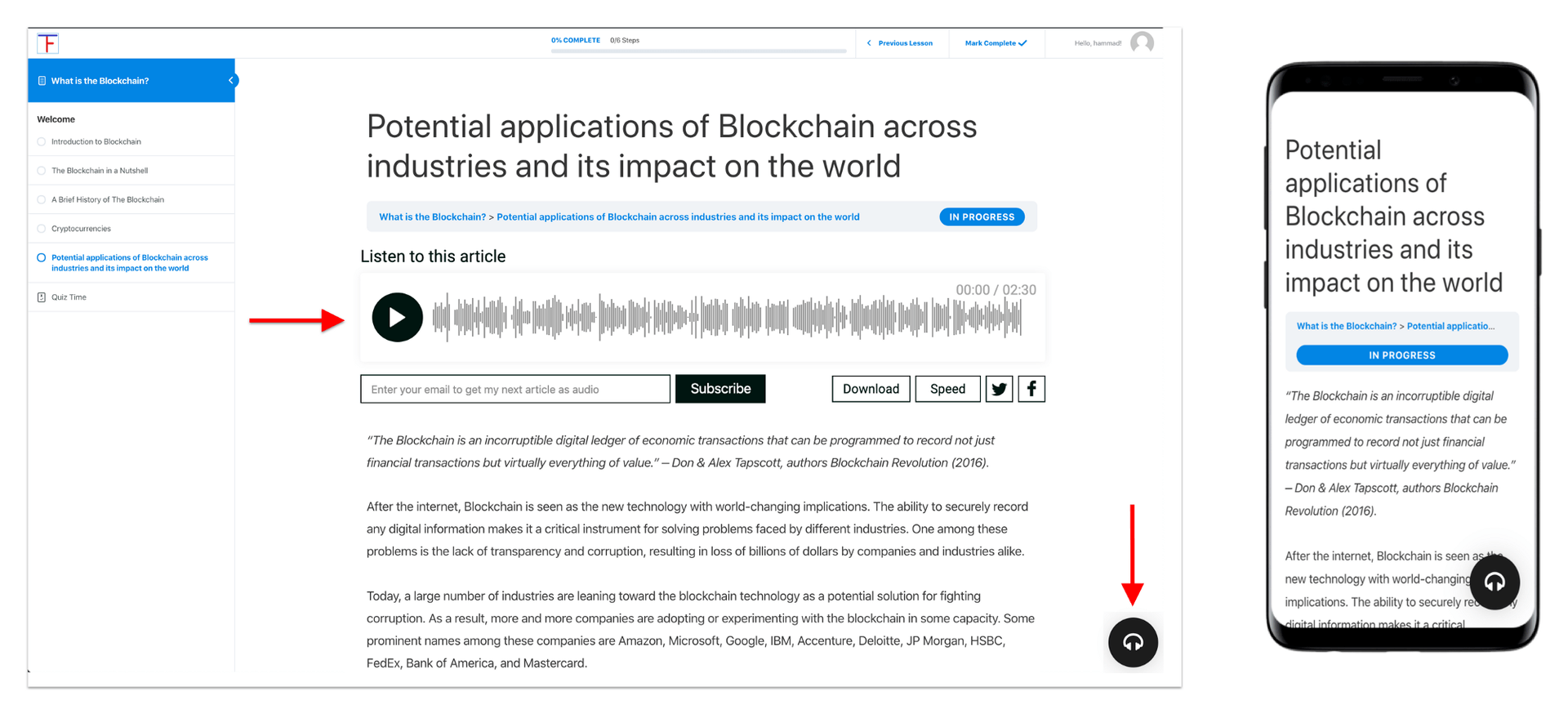
An even greater advantage of offering an audio version of the text is that it helps students who suffer from blindness, dyslexia, or other cognitive and learning disabilities who need to hear and see the text to learn.
2. Create Audio Translations In Different Languages
Online courses usually cater to a diverse demographic of students with different first languages, and it’s not always easy to learn in a second or a third language. Some students might not even be able to read in the written language.
Translating the course content into different languages and offering it in audio would help students better understand because research shows that students who are taught in both non-native and their native language comprehend better and remember for longer periods of time.
There are numerous translation services, both offline and online, that can help with translating your course content. Once you have the translated content, you can simply select the desired AI voices from 50+ languages and create the translated audio version.
3. Highlight Words To Provide An Immersive Learning Experience

Highlighting text while it is read aloud helps people with cognitive, learning, and language disabilities, as well as those with low literacy, to learn words and follow the flow of both the visual text and the spoken text. A lot of students prefer listening and being able to listen and follow along while reading. This offers a focused and immersive learning experience that triggers both audio and visual cognitive processes.
Highlighting words also helps students keep track of where they are in the current session in case they are listening to the content while multitasking (i.e., exercising, commuting, or washing dishes). They can quickly find the sentence that is currently being read and take control from there. Couple this with speed control that offers an assistive-interactive learning experience that students can take advantage of to learn at their own pace.
4. Settings To Seek And Control The Speed Of Listening
Similar to reading, the speed of listening varies from student to student. Providing a way to control the speed of audio is a great way to enhance the learning experience and cater to different learning styles.
Almost all AI voices support these playback speeds: very slow, slow, normal, fast, and very fast. Native speakers of the written language might naturally adjust themselves to faster listening speeds, whereas non-native speakers might gravitate toward slower listening speeds. Controls to seek the audio content back and forth in steps of 10-15 seconds offer a quick way to either skip or re-listen to what was just read, helping them either in memorization or better understanding.
5. Create An Audio Playlist Of Lessons And Key Concepts
Just like podcasts and music, creating an audio playlist of your course content can help students absorb more information in the same amount of time compared to reading which requires more concentration and cognitive bandwidth than listening.
Playlists can also help students revise their course or key portions of the course depending on how the playlists are categorized.
A neat hack to host playlists can be using podcast RSS feeds. These are essentially hosted XML used for distributing podcast episodes but can very well be used for distributing your course’s audio content that students can listen to or download as podcasts using their favorite podcast apps.
Conclusion
Today, audio is a mainstream channel for content consumption on the internet. Consumers demand and expect information to be available and accessible in different formats including audio, video and text, and eLearning courses are no exception.
Making your eLearning courses accessible through audio will not only benefit your students but you as a course creator as well.

